projections of the stars and gas in a simulated Milky Way-like halo (FOGGIE simulations)
Research Highlights
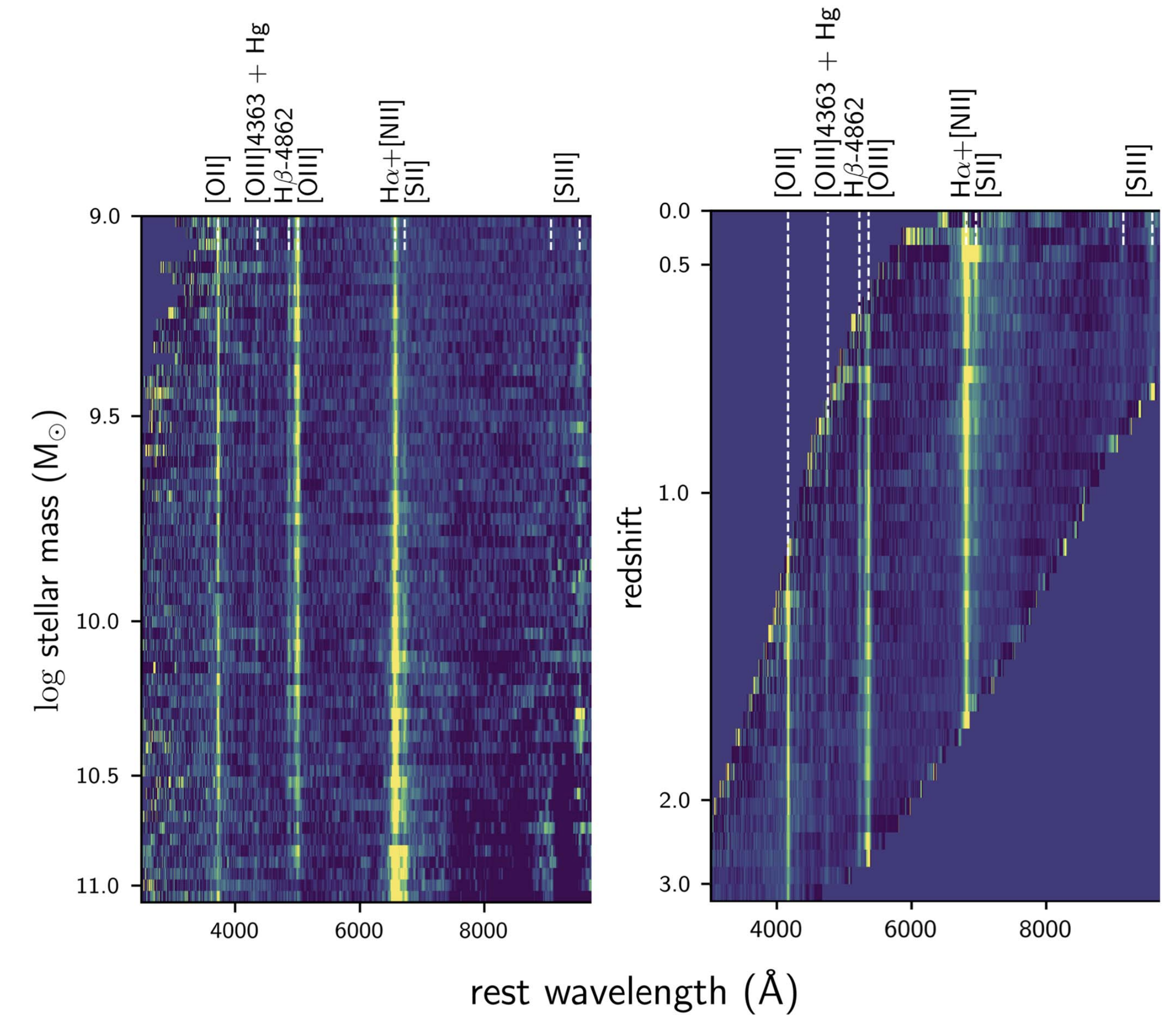
CLEAR: Survey Overview, Data Analysis, and Products
RCS et al., 2023, ApJS, 226, 22, ADS Link
This is the public release of high-level science products from the CLEAR survey — a 130-hour grism spectroscopy program with the Hubble Space Telescope. The products include redshifts, emission line fluxes, photometric catalogs, and 1D + 2D spectra for over 6000 galaxies over 0 < z < 3. The release is hosted on MAST.
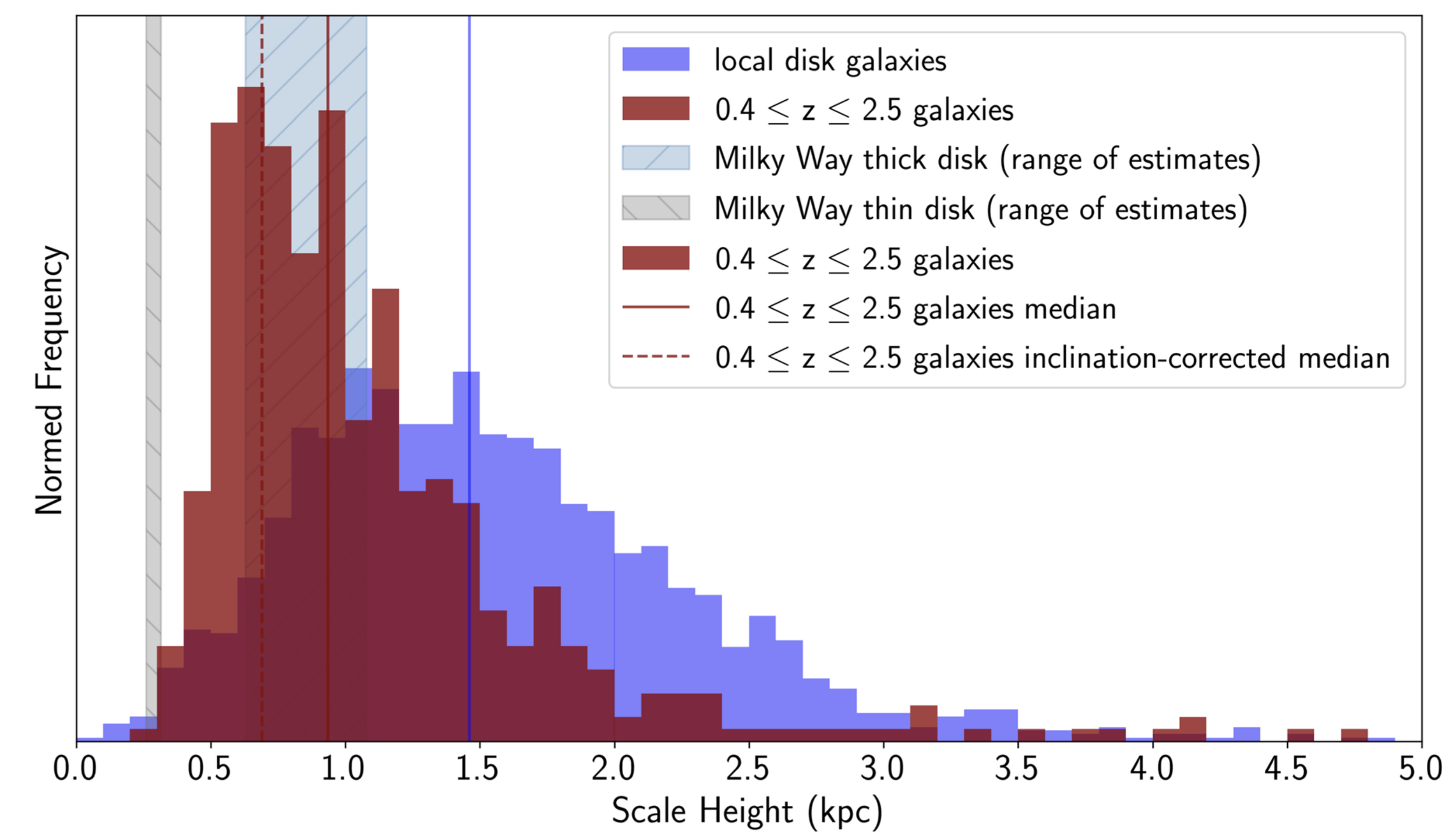
The Physical Thickness of Disks to z~2
Hamilton-Campos, RCS et al., 2023, ApJ, 956, 2, ADS Link
This paper, led by JHU graduate student Kathleen Hamilton-Campos (now APL), presents a first census of the physical thickness of disks from z = 2.5 to the present day. We find evidence that galaxy populations like that of the Milky Way’s progenitor on average thickened in the past ~11 Gyr. This could explain why older stars in the Milky Way and other disks generally lie at large heights above their galaxy midplanes (i.e., the age-sigma relation). We also find that galaxies as thick as the Milky Way’s thick disk were already in place at these early times. It’s a great paper — check it out.
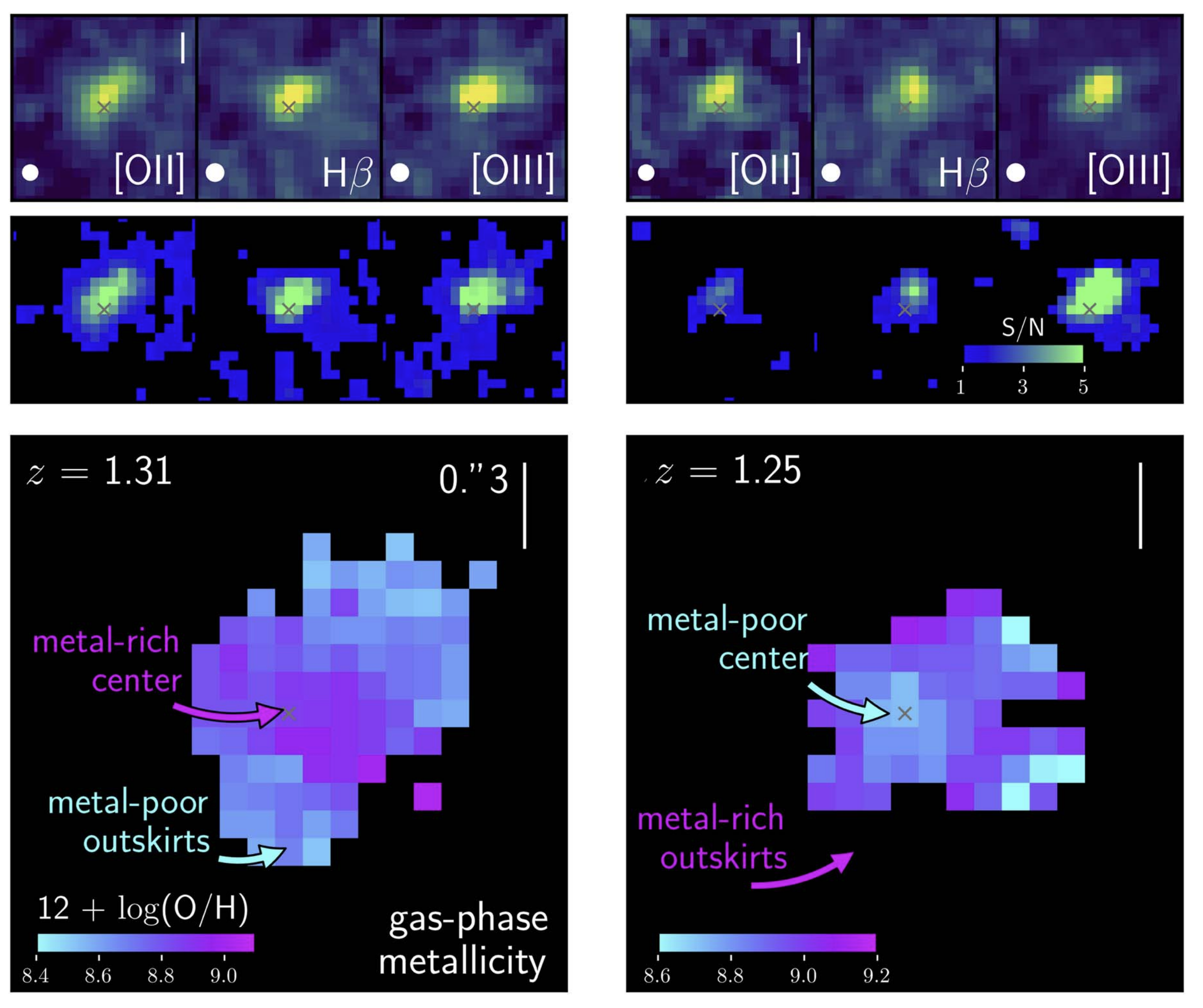
The Gas-phase Metallicity Gradients of Star-forming Galaxies at 0.6 < z < 2.6
RCS et al., 2021, ApJ, 923, 203, ADS Link
Here we present the gas-phase metallicity radial profiles of over 200 star-forming galaxies at 0.6 < z < 2.6, measured through deep near-infrared Hubble Space Telescope slitless spectroscopy. Surprisingly, we find that the majority of these profiles are either flat or positive. Flat and positive gradients are unexpected given the star-formation profiles in these galaxies. We show that these results can only be reconciled if metals are being rapidly re-distributed around galaxies at this redshift.
FOGGIE: The Stochasticity of Ram Pressure Stripping in Galactic Halos
RCS et al., 2020, ApJ, 905, 2, ADS Link and Newsletter
Here we studied ram pressure stripping and satellite quenching in cosmological simulations from the FOGGIE suite. We show that the high contrast in the density and kinematics of the circumgalactic medium (CGM) around Milky-Way like galaxies leads to stochastic and unpredictable ram pressure stripping. This behavior is not captured by smooth hydrostatic models of the CGM. In short, environmental quenching of satellites is a dice roll.
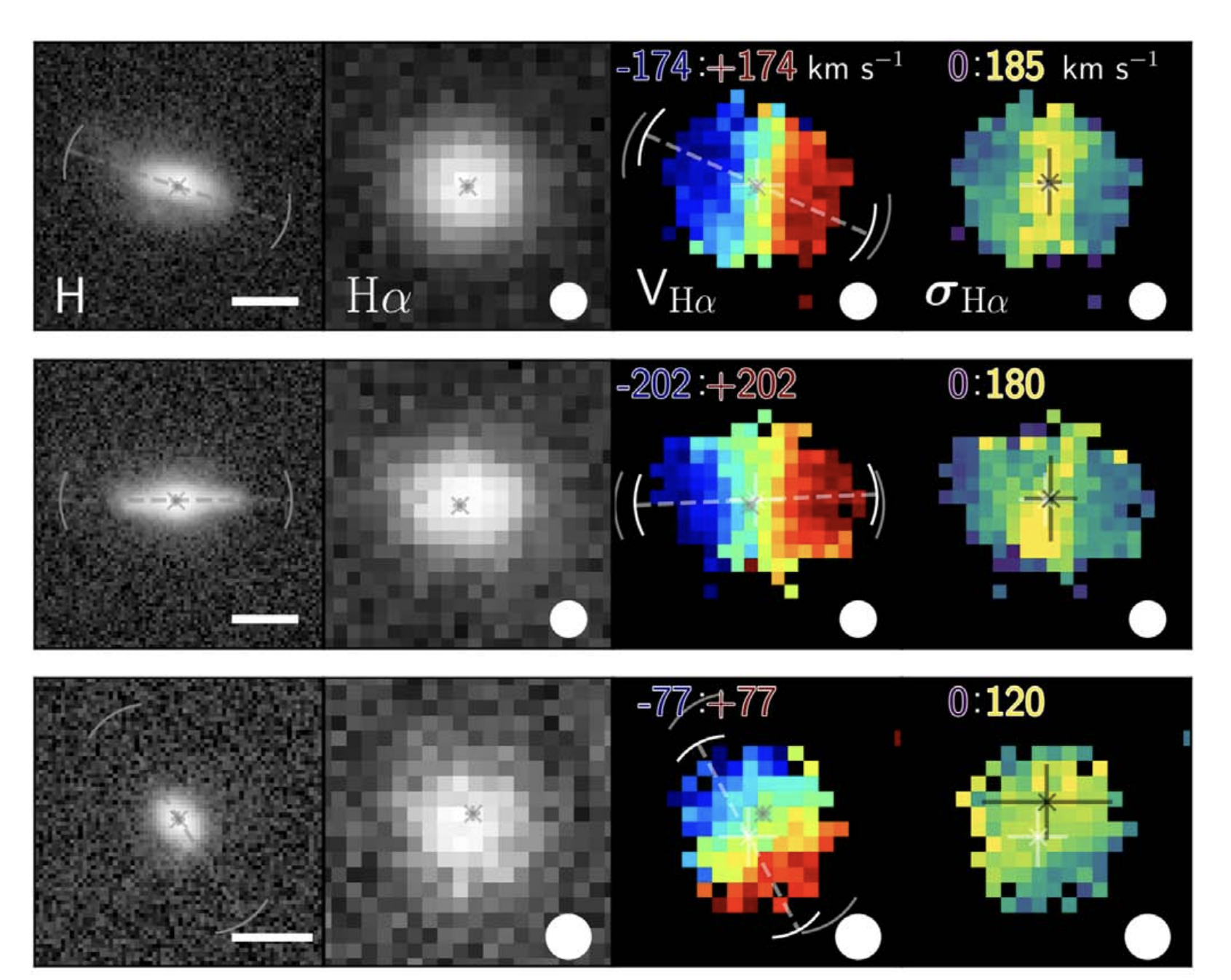
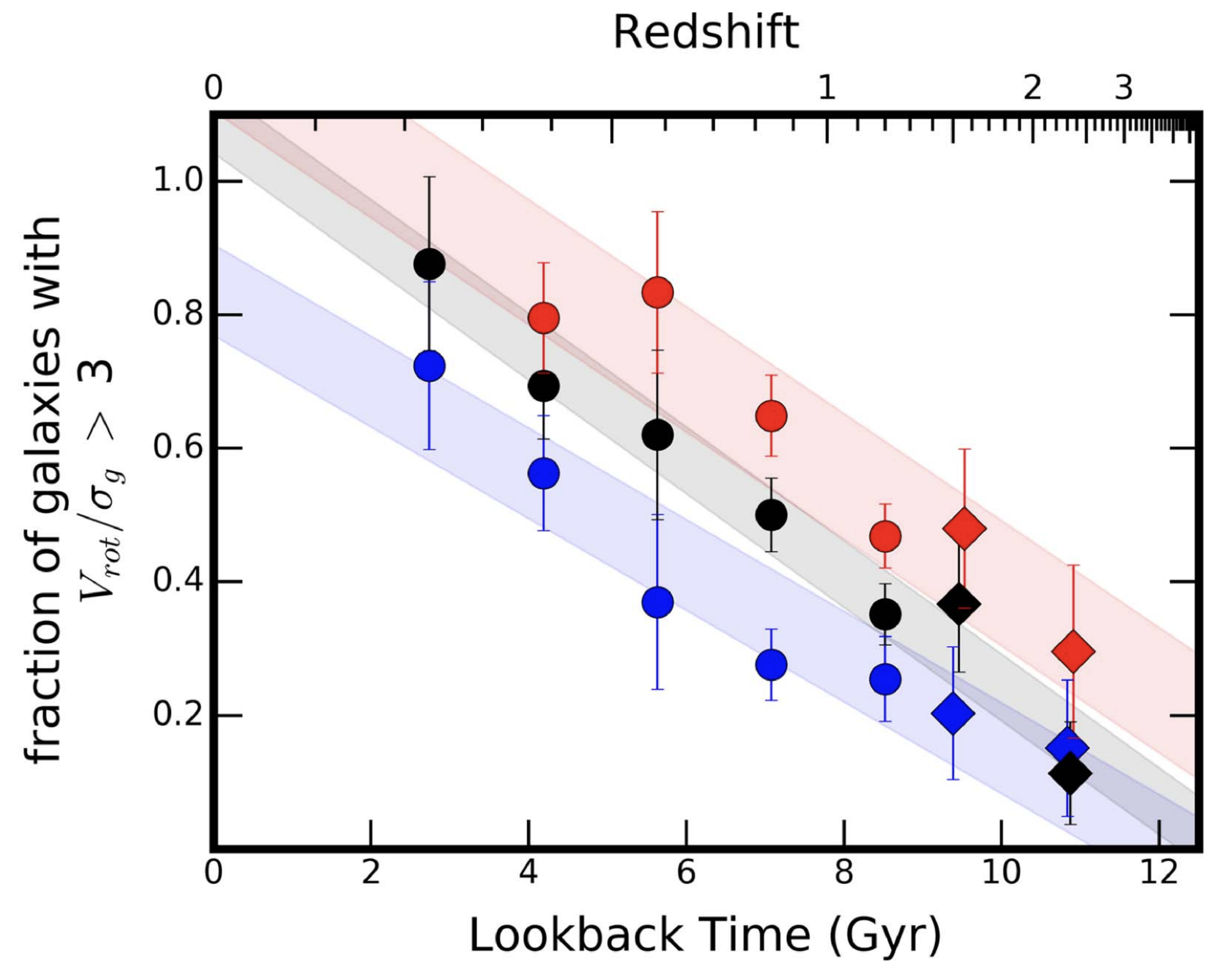
In this work, we measure the evolution of the internal gas kinematics of star-forming galaxies from the peak of cosmic star formation at z~2 to today. This sample covers a continuous baseline in redshift over 0.1 < z < 2.5, spanning 10 Gyr. We find that kinematically-ordered disk galaxies are rare at z ~ 2 at all masses.
Distinguishing Mergers and Disks in High-redshift Observations of Galaxy Kinematics
RCS et al., 2019, ApJ, 874, 1, ADS Link
The majority of massive star-forming galaxies at z ∼ 2 have velocity gradients suggestive of rotation, in addition to large amounts of disordered motions. However, there is a significant challenge in interpreting these data: galaxy mergers and rotating disk galaxies are indistinguishable at the typically low spatial resolution available from the ground. In this work, we generate ~24,000 synthetic images and kinematic maps of cosmological simulations to quantify this bias for real observations. The synthetic images created from this work are available on MAST.
Assembly of Disk Galaxies from z~2 to Today
RCS et al., 2017, ApJ, 843, 46, ADS Link
In this work, we use kinematic measurements from the DEEP2 survey (Kassin+07) to study the Tully-Fisher Relation (TFR) in the local universe. We find that today’s low mass galaxy population exhibits significant scatter in rotation velocity. We argue that a significant fraction of low mass galaxies today have not yet formed a settled rotating disk. We mark a specific mass above which nearly every galaxy today has formed a disk.
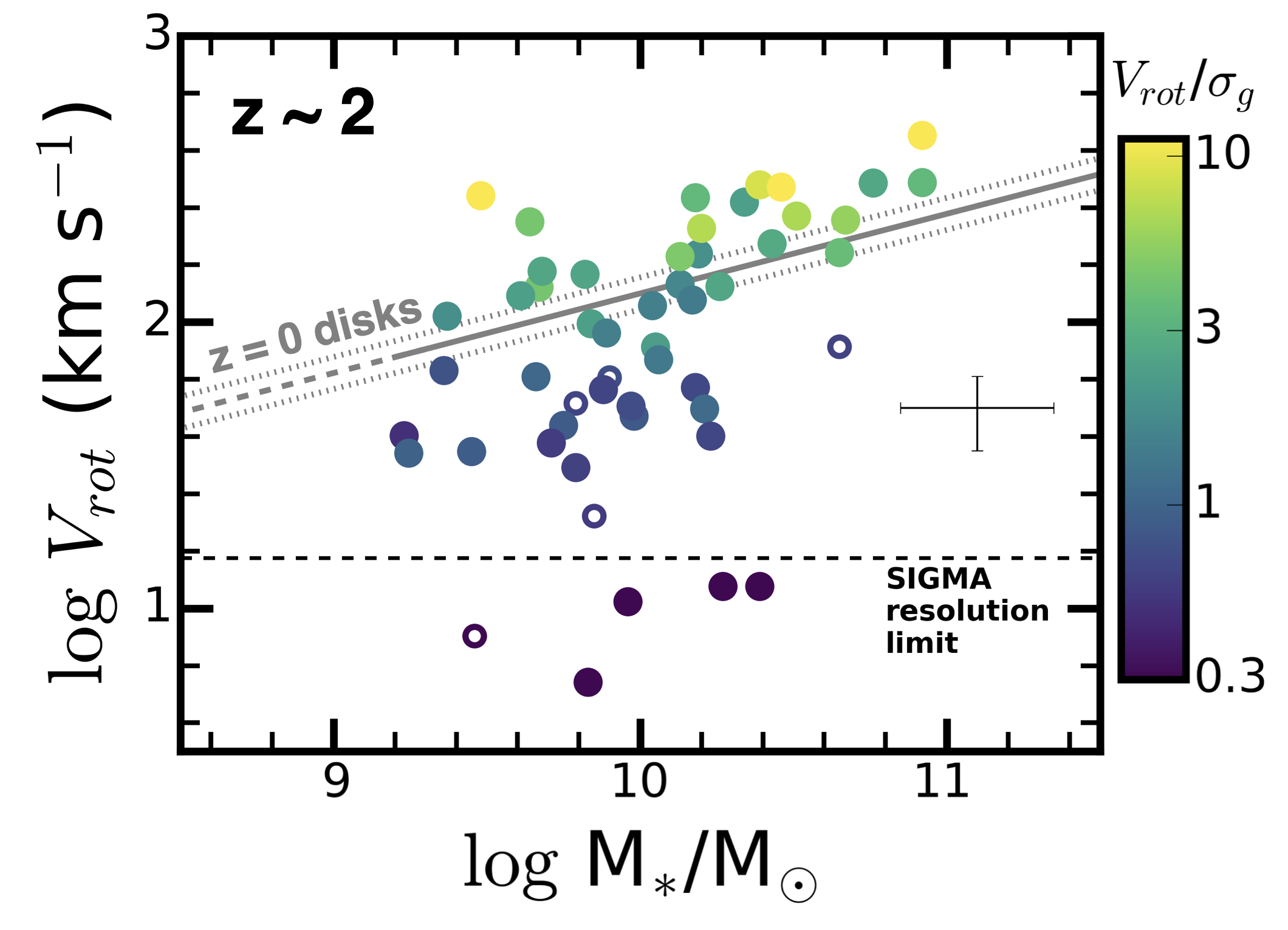
Kinematic Downsizing at z~2
RCS et al., 2016, ApJ, 830, 1, ADS Link
This work presents the SIGMA survey and reports on the kinematics of typical star-forming galaxies at z~2. We find a significant fraction of low-mass galaxies (progenitors of the Milky Way) are dispersion dominated and inconsistent with standard models of turbulent disks.
A Transition Mass in the Local Tully-Fisher Relation
RCS et al., 2015, MNRAS, 452, 986, ADS Link